Javascript Flow Processor
Purpose
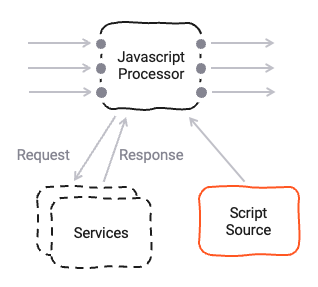
The Javascript Asset allows you to define detailed business logic which you may want to apply to a flow of messages. Here are some examples:
- Convert message data from one format to another
- Filter information based on specific rules
- Enrich individual data using specific rules and/or external data sources (e.g. reference data)
- Route messages based on your own criteria
- Gather metrics and statistics, and store and forward them to other targets
and basically anything else you can imagine here.
Prerequisites
You need:
- A Source Script which should be executed within this asset.
- Knowledge on how to work with Javascript in layline.io. Please check the Javascript Language Reference to learn about this.
Configuration
Name & Description
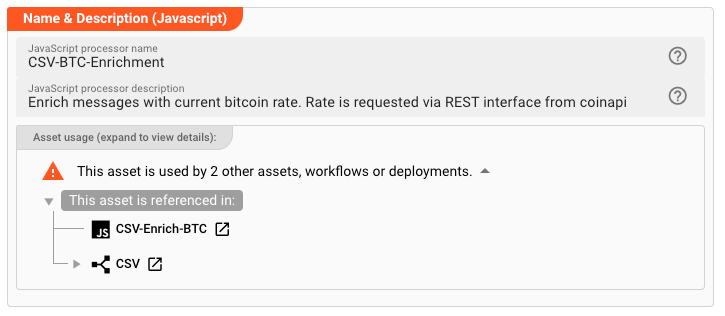
-
Name: Name of the Asset. Spaces are not allowed in the name. -
Description: Enter a description.
The Asset Usage box shows how many times this Asset is used and which parts are referencing it. Click to expand
and then click to follow, if any.
Asset Dependencies
Use this section to add Formats which you plan to use as part of your filtering and routing rules.
Why do I have to add formats here?
Doesn't the system know which Formats I am using?
layline.io automatically understands when you are using Formats as part of your input and output processors and automatically mounts them at runtime.
But when you are referencing Formats which are not used as part of an input or output Processor directly, but rather referenced in
a Javascript Flow Processor or Quickscript, then the system may not be aware that you are using this format within
any of those scripts.
This would result in a runtime error.
To avoid this, you can explicitly mention the Formats you are referencing in your scripts. This ensures, that these Formats will always be mounted at runtime. So it is best practice to add Formats which are referenced in this Asset here.
To add formats click on Add Dependency and select the Format you wish to add as a dependency.
Repeat for any other Format dependency.
Input Ports
This Processor can have one or more input ports from which it receives data to process. It must have at least one input port, however.
A port can have a name and description. Names must exist and be unique within the Processor.
You can add an input port by clicking on Add Port, or remove an input port by clicking on Delete.
You cannot delete the port if it is the last one within the processor.
Output Ports
This Processor can have one-to-many Output Ports to send messages on within the Workflow.
A port can have a name and description. Names must exist and be unique within the processor.
Root Script
The Javascript Asset obviously needs a Script to be executed. Prior to version 1.0 of layline.io the Script was
configured as part of this Asset. Starting with v1.0 all Scripts are defined in the Sources tab of the project (2):
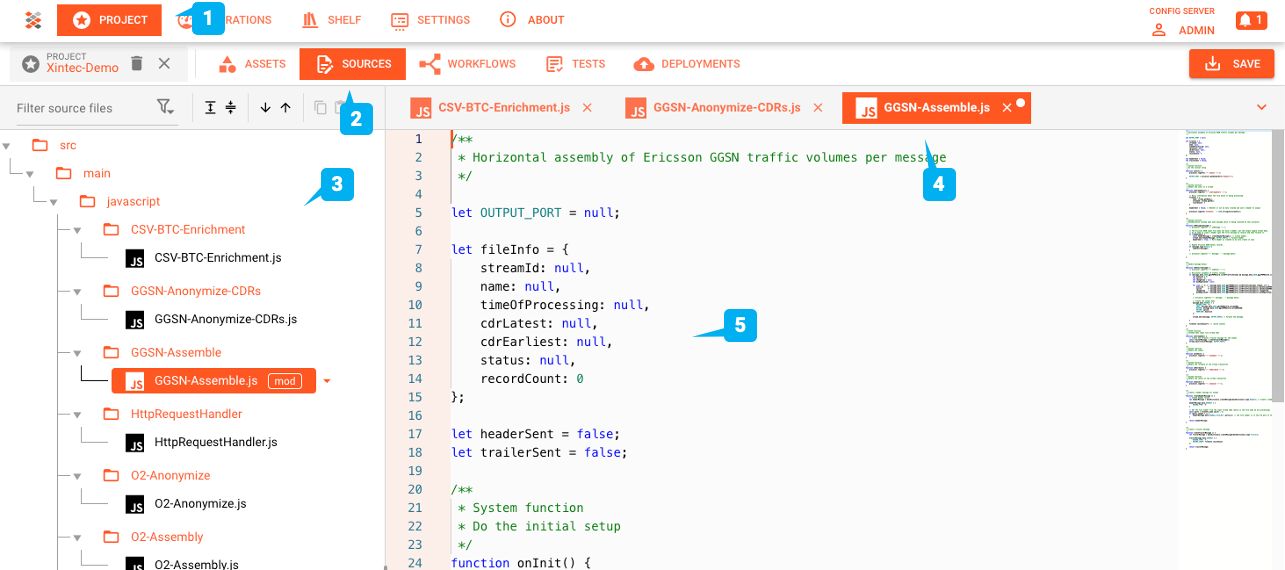
The root script to be executed within this Asset is then selected here:
To understand how a Source must be structured to work in a Javascript Asset, please consult the Javascript Language Reference.
Service Mappings
Javascripts may make use of Services which you may have configured here. These methods could be database operations, HTTP-request and whatever else Services do provide.
Let's say your Javascript invokes an HTTP-Service which provides a method to retrieve the current Bitcoin price via a
REST-Api. Let's also assume that the name of the Service to be linked is BTCService.
- Add a Service Mapping by clicking on
Add Service Mapping(1). - Select the Service which you want to map (2).
- Provide a
Logical Service Name. This is the name by which the Service is used in the underlying Javascript! If the name you enter here, is different to what you are using in your script, the script will not recognize the Service.

Arguments
You can pass arguments to the assigned script. This may be useful when reusing the same script in various different
Javascript Assets and Workflows, but the script should behave slightly different in each of those instances.
Passing arguments from a Javascript Asset to can provide this functionality. Please check the getArguments()
method here, on how to retrieve arguments in the script.

In case you are entering arguments (1), the editor will check for valid JSON and outline this in case it is invalid.
You can format the JSON entries with a click on Format JSON (2).
Entering invalid JSON will cause problems when using the Arguments in the underlying script.
Failure Handling
Processing within a Flow Processor like this one can fail for various reasons. In this section you can define how the system should behave in case of such problems.
Failure Types
Four types of failures are observable:
| # | Failure observables / Reaction | Ignore | Retry Event/Message | Retry Stream | Rollback Stream |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Stream start failure handlingA problem occurred in this Asset when starting a new stream. | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| 2 | Stream end failure handlingA problem occurred in this Asset when ending a stream. | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| 3 | Message failure handlingA problem occurred when handling a specific message in this Asset. | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| 4 | Rollback commit failure handlingA problem occurred during system issued rollback or commit procedure. | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
Failure Type Reactions
Each of these failure types can be responded to with four different reactions:
Ignore
Don't do anything.
Rollback Stream
Rollback the complete stream. In the case of batch/file processing for example the complete file (which represents the stream) will be rolled back and put into error.
A rollback signal will be issued to all participating Workflow Processors. Each Processor needs to ensure itself how to deal with a rollback. A Javascript Flow Processor, for example, which directly interacts with a database will have to react to a rollback signal:
export function onRollback() {
if (connection) {
try {
connection.rollbackTransaction();
connection.closeConnection();
} catch (err) {
} finally {
connection = null;
}
}
}
Retry Stream
Don't simply give up. Try to process the whole stream again. This option allows you to define how often and in what intervals the retries should be performed.
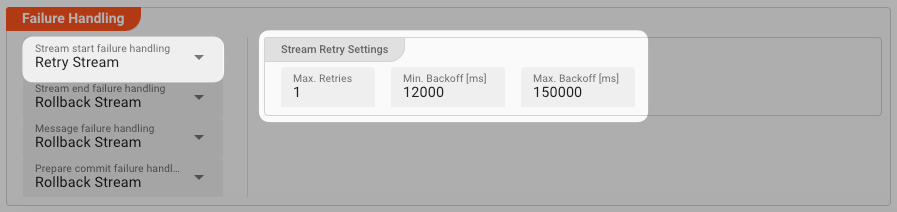
Stream Retry Settings
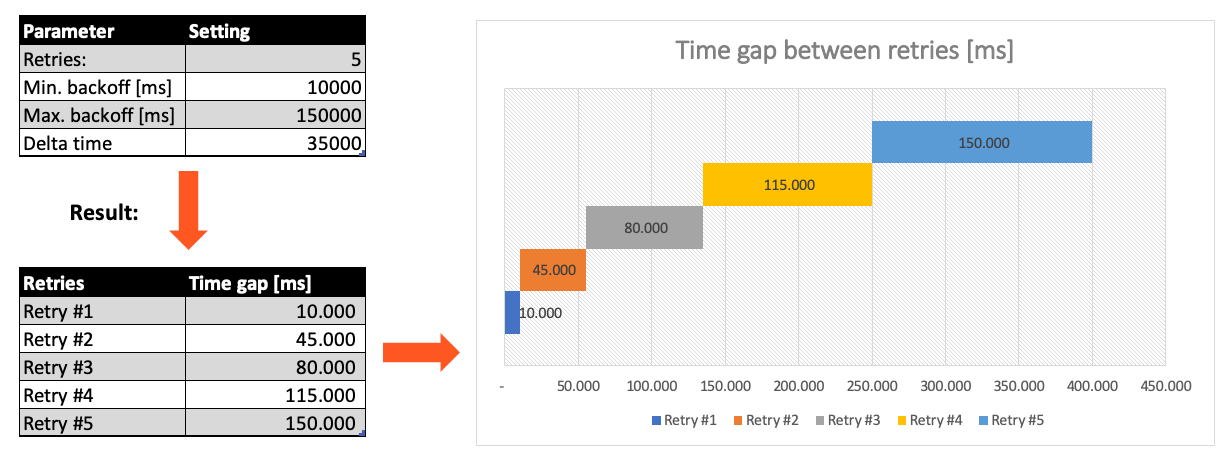
Max. Retries: The number of retries which should be performed. For example "5".Min. Backoff [ms]: Wait at least x milliseconds between each retry. For example "12000" (12 seconds).Max. Backoff [ms]: Wait at max x milliseconds between each retry. For example "150000" (150 seconds).
Based on these parameters, the system will try to balance the defined number of retries within the time boundaries of min. backoff and max. backoff. Taken the example numbers from above, the five retries would happen in this timespan:
Retry Event/Message
Pick this reaction if you want to retry processing the current message. As is the case with the Retry Stream reaction you can define how often and in what intervals the retries should be performed.
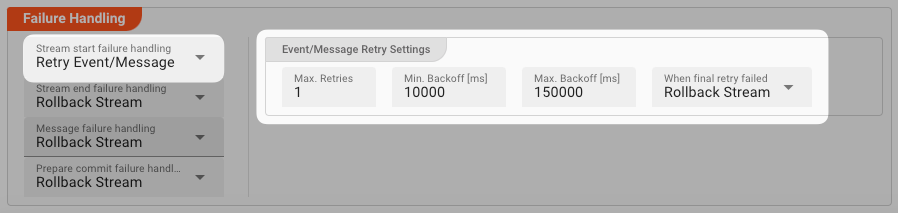
The settings are the same as with the Retry Stream reaction. So please refer to this.
There is one additional setting, however, which is When final retry failed.
You here have the option to decide what to do if the message cannot be processed, even after the final retry:
-
Ignore: Don't do anything. -
Rollback Stream: Fallback to rolling back the whole stream. -
Retry Stream: Retry the whole stream once again. If you pick this option, then you can again define all relevant Retry Stream parameters.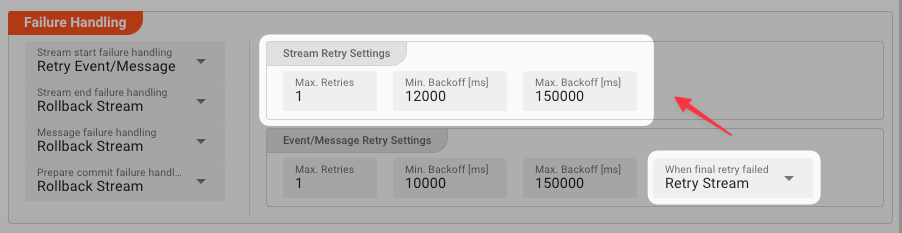
A Workflow has one Input Processor which is responsible for reading data from a Source. Sources are for example files, databases, or message queues.
The settings for Retry Event/Message and Retry Stream only work for specific Source Types which a Workflow uses.
These are:
Please note, that the creation of the online documentation is Work-In-Progress. It is constantly being updated. should you have questions or suggestions, please don't hesitate to contact us at support@layline.io .