Source S3
Purpose
Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) is an object storage service that offers industry-leading scalability, data availability, security, and performance. Next to Amazon's S3 there are now various object storage providers which grant S3 compatible access to their storage solutions as well (e.g. Google Cloud Storage, IONOS, et al).
This UI helps to define the specific bucket and folder source of an S3 connected endpoint.
This Asset can be used by:
| Asset type | Link |
|---|---|
| Input Processors | Stream Input Processor |
Prerequisite
You need:
Configuration
Name & Description
Name : Name of the Asset. Spaces are not allowed in the name.
Description : Enter a description.
The Asset Usage box shows how many times this Asset is used and which parts are referencing it. Click to expand and then click to follow, if any.
Required roles
In case you are deploying to a Cluster which is running (a) Reactive Engine Nodes which have (b) specific Roles configured, then you can restrict use of this Asset to those Nodes with matching roles.
If you want this restriction, then enter the names of the Required Roles here. Otherwise, leave empty to match all Nodes (no restriction).
Throttling & Failure Handling
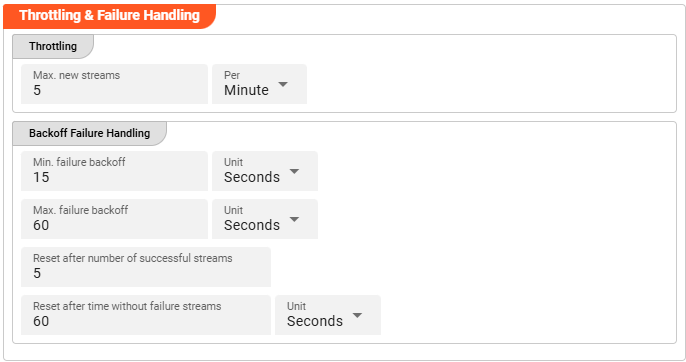
Throttling
The following parameters allow to control the maximum number of new stream creations per given time period.
Max. new streams: Maximum number of streams this source is supposed to open resp. process within a given time period.Per: Time interval unit for the providedMax. new streamsnumber from the drop-down list.
Configuration values for this parameter are dependent on the use case scenario. Assuming your data arrives in low frequency cycles these values are negligible. In scenarios with many objects arriving in short time frames it is recommended to have a closer look on adapting the default values.
Backoff Failure Handling
These parameters define the backoff timing intervals in case of failures. Based on the following parameters, the system will step by step throttle down the processing cycle based on the time boundaries of min. failure backoff and max. failure backoff. It thereby allows to slow down the processing during failure scenarios.
Min. failure backoff: The minimum backoff time before the next source item processing (in case of failure scenario).Unit: The Unit that goes with the given minimum time value.Max. failure backoff: The maximum backoff time before the next source item processing (in case of failure scenario).Unit: The Unit that goes with the given maximum time value.
Based on these values the next processing will be delayed: starting with the min. failure backoff time interval the waiting time will be increased step by step up to the max. failure backoff.
Reset after number of successful streams: The backoff failure throttling reset.Reset after time without failure streams: Time-based reset for backoff failure throttling .Unit: The Unit that goes with the given time-based backoff failure throttling reset.
Whatever comes first will reset the failure scenario throttling after the system is back to successful stream processing.
Polling & Processing
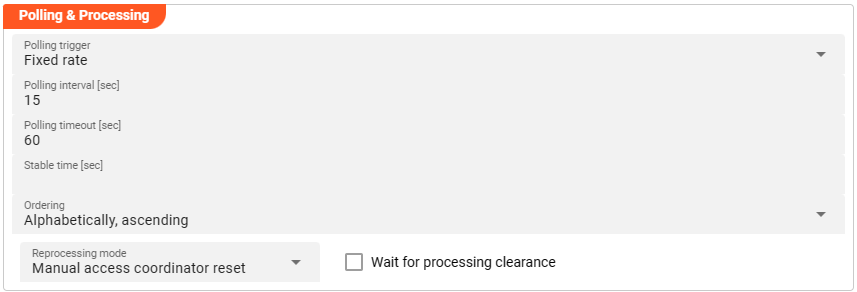
This source does not reflect a stream, but an object based storage source which does not signal the existence of new objects to observers. We therefore need to define how often we want to look-up (poll) the source for new objects to process.
You can choose between Fixed rate polling and Cron tab style polling:
Fixed rate
Use Fixed rate if you want to poll in constant and frequent intervals.
Polling interval [sec]: Enter the interval in seconds in which the configured source should be queried for new objects.
Cron tab
Use Cron tab if you want to poll at determined times. The Cron tab expression follows the cron tab style convention which may be familiar to you.
In all other cases you can read more about crontab and the syntax here.
You can simulate cron settings using this smart website.
Or you can use the Cron expression editor provided underneath the calendar symbol on the right hand side:
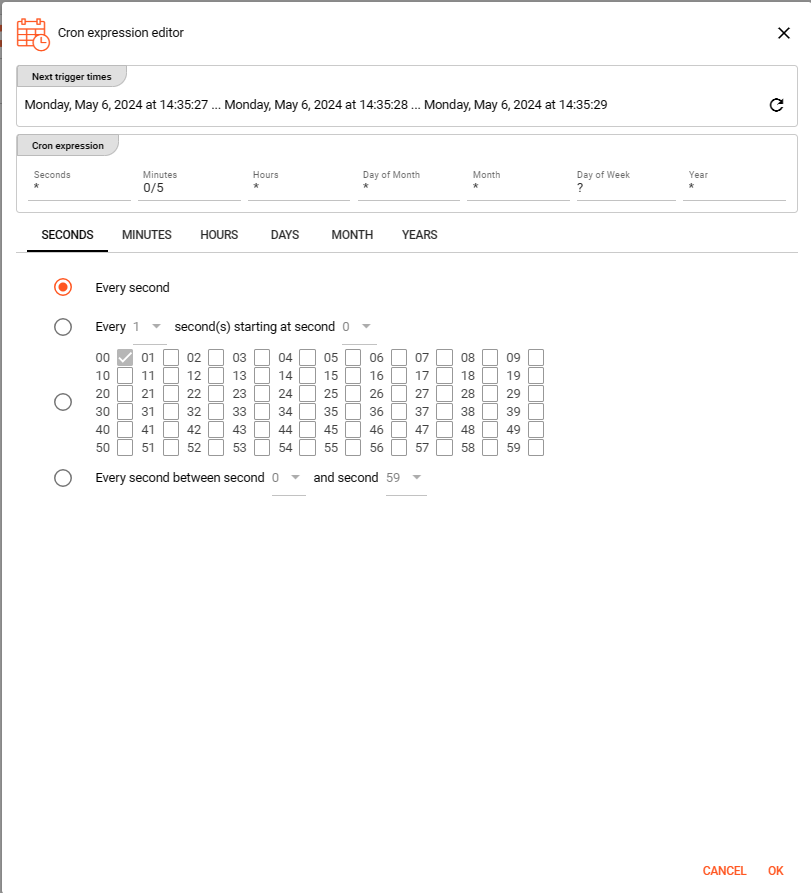
Configure your expression with the help of this editor. The Next trigger times at the top helps to visualize the configured expression. Press OK towards the end of this editor window to store the given values.
Polling timeout
The Polling timeout [sec] defines the time in seconds to wait until a polling request fails.
Depending on the endpoint and its responsiveness you may want to change this number to something higher or lower.
You should set it high enough, so that you are confident that the endpoint responds under normal operation.
Stable time
The Stable time [sec] defines the number of seconds that file statistics must stay unchanged for considering it as stable.
Configuring a value in here will check the appropriate file stability before processing the file.
Ordering
When listing objects from the source for processing, you can define in what order they should be processed. Pick one of the following self-explanatory settings:
Alphabetically, ascendingAlphabetically, descendingLast modified, ascendingLast modified, descending
Reprocessing mode
Configuring the Reprocessing mode relates to layline.io's Access Coordinator feature.
You can pick between three modes:

Manual access coordinator reset: any source element processed and stored in layline.io's history needs manual reset within the Sources Coordinator before reprocessing of a re-ingested source is performed (default mode).Automatic access coordinator reset: this mode allows the automatc reprocessig of already processed and re-ingested sources as soon as the respective input source has been moved into the configured done or error directory.When input changed: this mode behaves as described inManual access coordinator resetwhile it performs an additional check whether the source has potentially changed; i.e. the name of the source is identical but the content differs. In case the input in fact changed, the reprocessing will start without manual intervention.
Wait for processing clearance
Activating this checkbox identifies new input sources as Wait for processing clearance. This means, the input source
leaves unprocessed in the input directory until a) a manual intervention through Operations provides active clearance for processing the respective file or
b) some Javascript executes the AccessCoordinator.giveClearance(source: string, stream: string, timeout?: number) method.
S3 Connection
Select the previously configured AWS Connection to use for this Source.
S3 Bucket
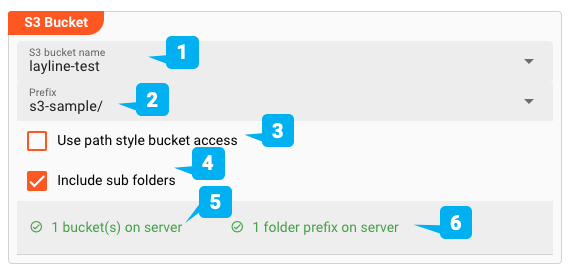
-
S3 bucket name (1): Once you picked a S3 Connection above the system will try to test the connection and list bucket names it can find. These will be available for selection here. You can check how many buckets could be found at (5) -
Prefix (2): If you pick a valid bucket (1), then available prefixes (folders) will be available for selection here. You can check how many prefixes could be found for a given bucket at (6) -
Use path style bucket access (3): The S3 API allows accessing objects via legacy "path style" or "virtual hosted style". Check this box if you want to access objects via legacy path style access. You can read more about this here -
Include sub folders (4): Check this box if you want sub-folders to be included when querying the source. This means that all objects from sub-folders within a bucket/prefix combination will be considered for processing.
While you are entering and changing S3 bucket parameters, layline.io frequently tries to connect to the endpoint and retrieve bucket and prefix information. The status of these attempts is displayed at the bottom of the group box.
In case of error, you can hover the mouse over the red output and view what the problem is:
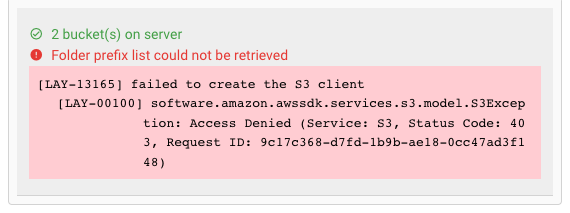
This usually helps to resolve the issue.
Related Topics
Internal
External
Potential problems
Please note, that the creation of the online documentation is Work-In-Progress. It is constantly being updated. should you have questions or suggestions, please don't hesitate to contact us at support@layline.io .