Services Introduction
Purpose of Services
Probably the easiest way to describe the concept of a service within layline.io, is to claim that Services that of an external function calls. Very similar to the notion of web services. Such a function call can read or write data, or for example call an actual web service, and more.
Services provide connection and access to specific types of interfaces. There is for example a Service specialized on conversing with JDBC compatible databases. Another type of Service is specialized on Aerospike NoSQL storage, and yet another one for dealing with HTTP/S calls, etc.
Apart from Email Service and Teams Service the connection to the appropriate backend is configured in the Service Asset itself and not through a dedicated Connection Asset.
How to put Services to work
Showcase
To explain how it all works together, we will construct an example. In this example we are processing telecommunication usage data. This usage data carries information which we will use to retrieve associated call type data from a database and enrich the usage data with that extra information.
Conceptually, this is what it looks like:
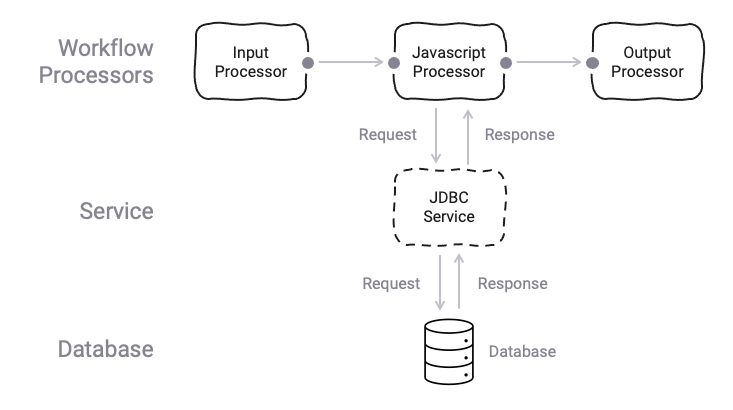
What's happening here, is that a Processor (JavaScript Processor in image) makes use of a Service (JDBC Service in image) in a request/response pattern.
Services are usually used from within Javascript Processor Assets.
Service configuration
First we define a service which accesses a JDBC database that holds the desired information.
We then tell the JDBC Service how to connect to the database (differs based on service type):

Next we create a function GetCallTypeData which retrieves a number of fields for a given CallType. The CallType by which we query the data from the database is contained in the telecoms usage data which is processed by the Workflow.
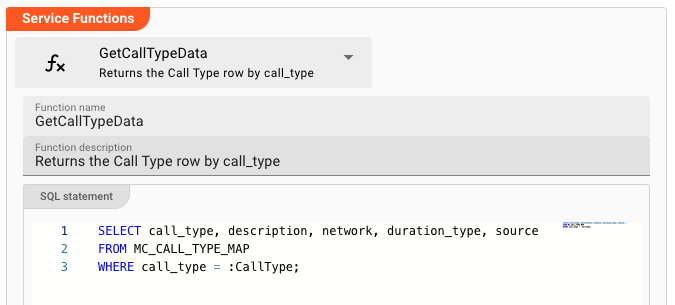
In the image you can see the related SQL-Statement. In line 3 we see the bind variable ":CallType" which must be filled for each usage data record processed. We will see how this works when look at the JavaScript Processor which invokes this Service.
This should be good enough explanation on how to set up this example Service. There is more to it which you can look up in the documentation of the specific service.
Using the Service
Now that we have set up the JDBC Service we can learn how it can be used. In the example, a JavaScript Processor in the Workflow will use the JDBC Service and invoke the function GetCallTypeData to get the related information from the database.
Let's give it a name:
We then tell the JavaScript Processor to use the Service which we have defined above. Unless we create this link in this way, we will be unable to reference the Service from within a Script:
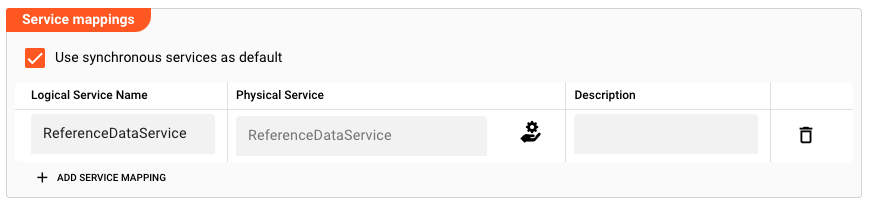
Note that we have to give the linke a logical name by which we reference the Service in the Script. This needs to be unique in case we link multiple different services to this same Processor. In our example we simply use the name of the linked Service also as the logical name ("ReferenceDataService").
We can now use the Service and the function which we have defined therein from within the JavaScript script:
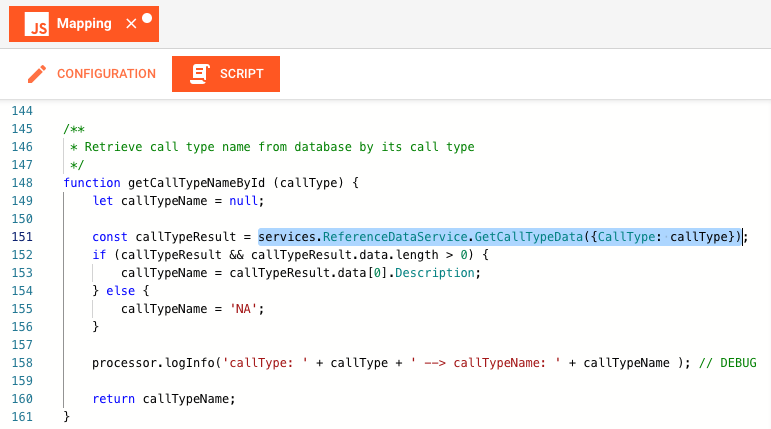
/**
* Retrieve call type name from database by its call type
*/
function getCallTypeNameByCallType (callType) {
let callTypeName = null;
// This is where we invoke the Service function.
// We pass the bind variable as a property within an object which we pass like so: {CallType: callType}.
// Make sure that the property name (CallType) is the same as defined in the Service.
const callTypeResult = services.ReferenceDataService.GetCallTypeData({CallType: callType});
// We then receive the result as an object.
// The structure of which is:
// callTypeResult: {
// data: [
// property1: value1,
// property2: value2,
// ...
// propertyn: valuen,
// ]
// }
if (callTypeResult && callTypeResult.data.length > 0) {
callTypeName = callTypeResult.data[0].Description;
} else {
callTypeName = 'NA';
}
processor.logInfo('callType: ' + callType + ' --> callTypeName: ' + callTypeName ); // DEBUG
return callTypeName;
}
Summary
In principle, this is how Services work and are being used.
It is important to know, that there may be slight variances between the different types of services. For example the return values of function calls may differ as well as how to reference function names, etc. This will be outlined in the documentation for each Service.
Please note, that the creation of the online documentation is Work-In-Progress. It is constantly being updated. should you have questions or suggestions, please don't hesitate to contact us at support@layline.io .